|
Why and How has PRSP progressed?
|
|
Since the late 1990s, poverty reduction has become an overarching goal for all economic assistance to low-income countries [see Table: Building International Consensus on Poverty Reduction from 1990 to Date].
 This is brought by the awareness of : This is brought by the awareness of :
- Increased international interest on poverty reduction under the recognition that poverty and inequality are still wide-spread phenomenon;
- Multi-dimensional understanding of poverty which has become widely accepted (income plus opportunity, capacities, security, empowerment).
 Such awareness, together with the questions about aid effectiveness, has led to the following initiatives: Such awareness, together with the questions about aid effectiveness, has led to the following initiatives:
- Result-oriented approach with quantified objectives, integrating a series of goals agreed at UN international conferences in the 1990s into the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) during 2000-2001;
- Comprehensive and partnership approach, as concretized in the World Bank's Comprehensive Development Framework (CDF) proposed by President Wolfenson in January 1999;
- Enhanced Heavily Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) Initiative, agreed at the Koln Summit in June 1999, as a more substantial, enhanced debt relief program for low-income countries.
 In parallel with these initiatives, it was agreed at the Annual Meetings of the World Bank/IMF in September 1999 that the Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (PRSP) would be prepared by the governments of low-income countries to serve as a basis for: In parallel with these initiatives, it was agreed at the Annual Meetings of the World Bank/IMF in September 1999 that the Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper (PRSP) would be prepared by the governments of low-income countries to serve as a basis for:
- A framework for development;
- Eligibility for debt relief under the Enhanced HIPC Initiative; and
- Eligibility for concessional assistance from the World Bank (IDA) and the IMF.
|
|
Who prepares PRSP?
|
|
 Low-income countries wishing to access concessional assistance from the World Bank and the IMF: more than 60 countries are currently engaged in the PRSP process. (*There are 80 countries eligible for IDA lending, of which 76 currently receive IDA support.) Low-income countries wishing to access concessional assistance from the World Bank and the IMF: more than 60 countries are currently engaged in the PRSP process. (*There are 80 countries eligible for IDA lending, of which 76 currently receive IDA support.)
 Heavily indebted, low-income countries wishing to qualify for the Enhanced HIPC Initiative: 42 countries (all of which are included in the above 60 countries) in the PRSP process. Heavily indebted, low-income countries wishing to qualify for the Enhanced HIPC Initiative: 42 countries (all of which are included in the above 60 countries) in the PRSP process.
Note: To avoid delays in approval of concessional loans or eligibility decision on the Enhanced HIPC Initiative, PRSP countries can prepare an Interim-PRSP before they elaborate a Full-PRSP.
|
|
What are concrete contents of PRSP?
|
|
The World Bank's background paper [World Bank 1999] indicates key principles of the PRSP. Its Source Book [World Bank 2001] provides detailed contents as a reference (see figure: PRSP Principles, Cycle, Contents and Assessment):
 Building on the CDF approach, the PRSP is guided by the following principles (as indicated in the parenthesis below): Building on the CDF approach, the PRSP is guided by the following principles (as indicated in the parenthesis below):
- Comprehensiveness of its content to cover country's macroeconomic, structural and social policies (comprehensive and prioritized);
- Consistency in the planning, implementation, evaluation cycle based on poverty diagnosis with measurable goals and indicators (long-term in perspective and results oriented);
- Broad-based participation of both internal stakeholders and donor communities in each stage of the cycle above mentioned (country-driven with participation and partnership).
 Once PRSP has been elaborated, Joint Staff Assessment (by the World Bank and the IMF) reviews the PRSP contents and process in light of: Once PRSP has been elaborated, Joint Staff Assessment (by the World Bank and the IMF) reviews the PRSP contents and process in light of:
- Participatory process;
- Poverty diagnosis;
- Goals/indicators/targets and monitoring/evaluation system; and
- Priority public actions.
|
|
How are the PRSP used?
|
|
 The PRSP is becoming the main tool for policy planning, i.e., budgeting, prioritizing, project selection, evaluation. Once agreed, PRSP may strongly bind the overall socio-economic policy framework of a particular country. The PRSP is becoming the main tool for policy planning, i.e., budgeting, prioritizing, project selection, evaluation. Once agreed, PRSP may strongly bind the overall socio-economic policy framework of a particular country.
 Moreover, the PRSP is used as the basis for donor coordination. Many donors use it as the basis of their country assistance strategy and align their aid resources to PRSP priority. Moreover, the PRSP is used as the basis for donor coordination. Many donors use it as the basis of their country assistance strategy and align their aid resources to PRSP priority.
|
|
Progress to date:
|
|
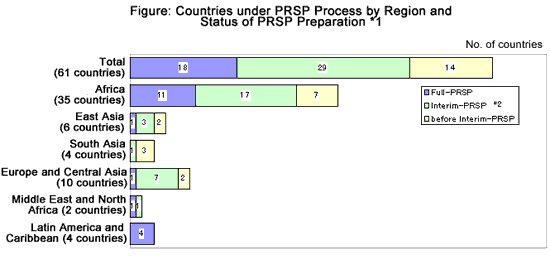
 18 countries completed Full-PRSP, and a total of 44 countries finished Interim-PRSP as of August 2002. Among the 44 countries, 29 have finished only Interim-PRSP [see Figure: Countries under PRSP Process by Region and Status of PRSP Preparation]. 18 countries completed Full-PRSP, and a total of 44 countries finished Interim-PRSP as of August 2002. Among the 44 countries, 29 have finished only Interim-PRSP [see Figure: Countries under PRSP Process by Region and Status of PRSP Preparation].
 The World Bank and the IMF undertook a comprehensive review in early 2002. The review report confirms the validity of the PRSP approach. At the same time, it recognizes the need for the flexibility in the PRSP approach respecting country-specific circumstances, and provides a number of "good practices" in the current PRSP process [see Box: Review of Early Experience of PRSP]. The World Bank and the IMF undertook a comprehensive review in early 2002. The review report confirms the validity of the PRSP approach. At the same time, it recognizes the need for the flexibility in the PRSP approach respecting country-specific circumstances, and provides a number of "good practices" in the current PRSP process [see Box: Review of Early Experience of PRSP].
|
| Note: |
*1 The 61 selected countries and their PRSP progress are calculated based on the data available at the World Bank's PRSP website at August 2002. These statuses are subject to constant revision as each country make progresses.
*2 including those countries which have already completed Full PRSP. |
| Source: |
PRSP Website: "PRSP document library."
HIPC Website: "HIPC Initiative: Status of Country Cases Considered under the Initiative, July 2002," and "Grouping of HIPCs Under the Enhanced HIPC Initiative: Status as of July 2002."
|
|
|
|
Selected issues on the PRSP approach
|
|
 The World Bank recognizes the followings dilemma in the PRSP formulation process [World Bank 2002]. The World Bank recognizes the followings dilemma in the PRSP formulation process [World Bank 2002].
- Speed vs. ownership and quality;
- Comprehensiveness vs. prioritization;
- Content vs. process.
 The critique of PRSP includes: The critique of PRSP includes:
- The PRSP does not offer common understanding on ownership and participation, and therefore it cannot be a true process for enhancing national ownership and participation (e.g. Jublee 2000 in [IMF 2002]).
- The contents of PRSP are a simple recycling of previous policies of structural adjustment, and macroeconomic policy and poverty reduction remain two unconnected fields. (e.g. [Cling et al. 2002]).
- The recent UNCTAD paper stresses the need for policies to strengthen productive capacities and promote employment through trade and investment [UNCTAD 2002].
|
| References |
CLING et al. [2002], The PRSP Initiative: Old Wine in New Bottles? (Paper presented at Annual Bank Conference on Development Economics on June, 2002, OSLO, NORWAY). [http://wbln0018.worldbank.org/eurvp/web.nsf/Pages/Paper+by+Razafindrakoto/$File/RAZAFINDRAKOTO.PDF].
IMF [2002], Synopses of External Comments and Contributions, February. [http://www.imf.org/external/np/prspgen/review/2002/comm/syn.pdf].
IMF & World Bank [2001], Guideline for Joint Staff Assessment of a Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper, April 18. [http://poverty.worldbank.org/files/jsa%20guidelines.pdf].
UNCTAD[2002], The Least Developed Countries Report 2002: Escaping the Poverty Trap, June. [http://www.unctad.org/en/pub/ps1ldc02.en.htm].
World Bank [1999], Building Poverty Reduction Strategies in Developing Countries, September. [http://poverty.worldbank.org/files/building_english.pdf].
World Bank [2001], PRSP Source Book, draft for comments, June. [http://www.worldbank.org/poverty/strategies/chapters/preface/pref0618.pdf].
World Bank [2002], "PRSPs Origins, Key Challenges and Good Practices." (Presentation materials by John Page, Director of Poverty Reduction, World Bank, at the World Bank Tokyo Office Public Forum on PRSPs on July 15, 2002).
World Bank, "PRSP Website: Document Library." [http://poverty.worldbank.org/prsp/].
World Bank, "HIPC Website: Progress to Date." [http://www.worldbank.org/hipc/progress-to-date/progress-to-date.html].
*This note was written by GRIPS Development Forum.
|
![]() What is the PRSP?
What is the PRSP?![]() What is the PRSP?
What is the PRSP?